The sum of direct labor cost and manufacturing overhead cost is known as conversion cost. The sum of direct materials cost and direct labor cost is known as prime cost. Costs may be classified as manufacturing costs and non-manufacturing costs. Remember, these practices are just a starting point, and their applicability may vary depending on your specific industry or function. By implementing these strategies and adapting them to your unique circumstances, you can effectively manage non-manufacturing costs and optimize your overall operations.
Nonmanufacturing Costs at PepsiCo
We recommend https://www.bookstime.com/ taking our Practice Quiz next, and then continuing with the rest of our Nonmanufacturing Overhead materials (see the full outline below).
- One of the main financial statements (along with the statement of comprehensive income, balance sheet, statement of cash flows, and statement of stockholders’ equity).
- Therefore, you should always consult with accounting and tax professionals for assistance with your specific circumstances.
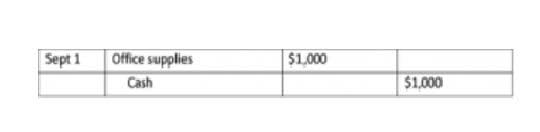
- The wood used to build tables and the hardware used to attach table legs would be considered direct materials.
- Cost of goods sold is usually the largest expense on the income statement of a company selling products or goods.
- From the perspective of activity-based costing (ABC), one approach is to identify cost drivers specific to service activities.
- Direct materials usually consists of a significant portion of total manufacturing cost.
- The balance sheet is also referred to as the Statement of Financial Position.
Non-Manufacturing Costs: Key For Accurate Costing
Product costs are the manufacturing costs that are considered to be a cost of a product. Insurance Expense, Wages Expense, Advertising Expense, Interest Expense are expenses matched with the period of time in the heading of the income statement. Under the accrual basis of accounting, the matching is NOT based on the date that the expenses are paid. Direct labor – cost of labor expended directly upon the nonmanufacturing costs materials to transform them into finished goods. Direct labor refers to salaries and wages of employees who work to convert the raw materials to finished goods.
- Even though nonmanufacturing overhead costs are not product costs according to GAAP, these expenses (along with product costs and profit) must be covered by the selling prices of a company’s products.
- However, if management wants to determine the profitability of a specific product or customer, it is necessary to allocate or assign nonmanufacturing costs to the products and/or customers outside of the financial statements.
- Items such as plastic parts, metal parts and paint can be examples of manufacturing inventory.
- This article looks at meaning of and differences between two main cost categories for a manufacturing entity – manufacturing cost and non-manufacturing cost.
Financial Reporting vs. Individual Products and Customers

The labor cost that can be physically and conveniently traced to a unit of finished product is called direct labor cost or touch labor cost. Examples of direct labor cost include labor cost of machine operators and painters in a manufacturing company. Like direct materials, it comprises of a significant portion of total manufacturing cost. The wood used to build tables and the hardware used to attach table legs would be considered direct materials. Small, inexpensive items like glue, nails, and masking tape are typically not included in direct materials because the cost of tracing these items to the product outweighs the benefit of having accurate cost data.
- Costs that are not related to the production of goods are called nonmanufacturing costs23; they are also referred to as period costs24.
- As product costs are assigned to inventory accounts initially, sometimes they are called inventoriable costs.
- However, for management objectives, managers frequently require the assignment of nonmanufacturing costs to goods.
- Like direct materials, it comprises of a significant portion of total manufacturing cost.
- Examples include advertising costs, salaries and commission of sales personnel, storage costs, shipping and delivery, and customer service.
Analyzing Overhead Costs in Service-Based Organizations

The direct materials would include the metal for the frame, tires, and handlebars. Manufacturing overhead might include the cost of factory utilities, depreciation on manufacturing equipment, and the salaries Online Accounting of factory supervisors. In the realm of managerial accounting, understanding the distinction between manufacturing costs and non-manufacturing costs is fundamental. These cost classifications not only aid in accurate financial reporting but also play a crucial role in internal decision-making processes. This section delves into the intricacies of these costs, providing you with the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of cost management effectively. Sometimes it is difficult to discern between manufacturing and non-manufacturing costs.

Manufacturing costs other than direct materials and direct labor are categorized as manufacturing overhead cost (also known as factory overhead costs). They usually include indirect materials, indirect labor, salary of supervisor, lighting, heat and insurance cost of factory etc. Mosly, manufacturing overhead costs cannot be easily traced to individual units of finished products. Even though nonmanufacturing overhead costs are not product costs according to GAAP, these expenses (along with product costs and profit) must be covered by the selling prices of a company’s products. In other words, selling prices must be large enough to cover SG&A expenses, interest expense, manufacturing overhead, direct labor, direct materials, and profit. Factory overhead – also called manufacturing overhead, refers to all costs other than direct materials and direct labor spent in the production of finished goods.
